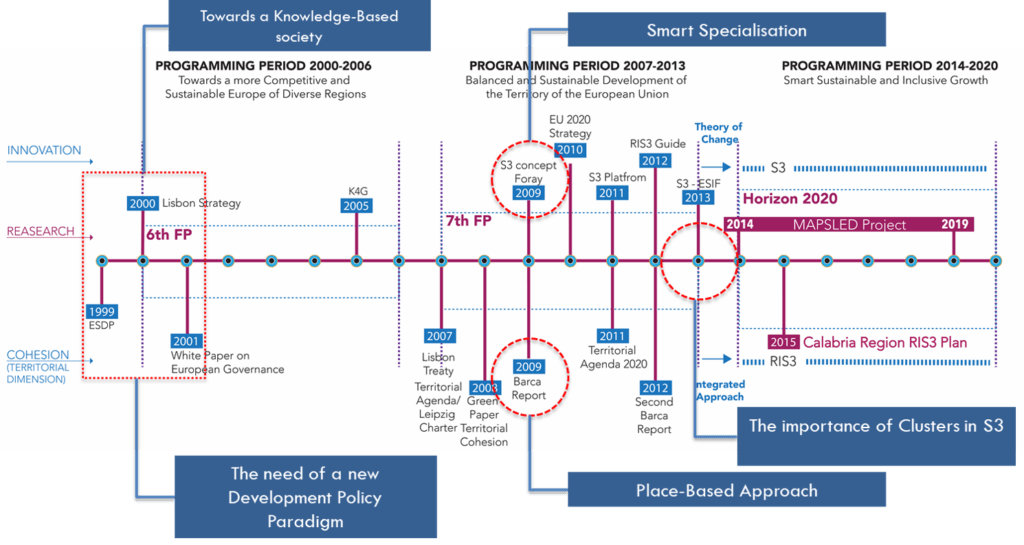
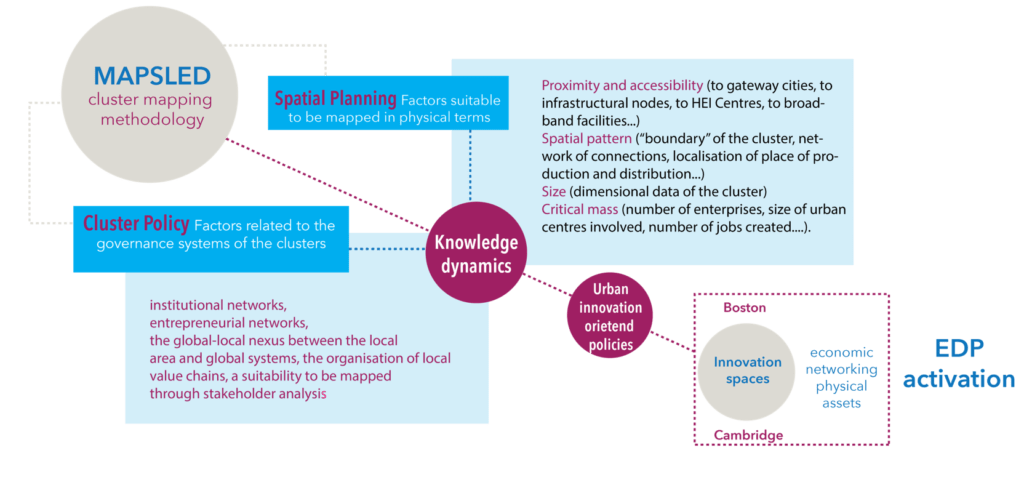
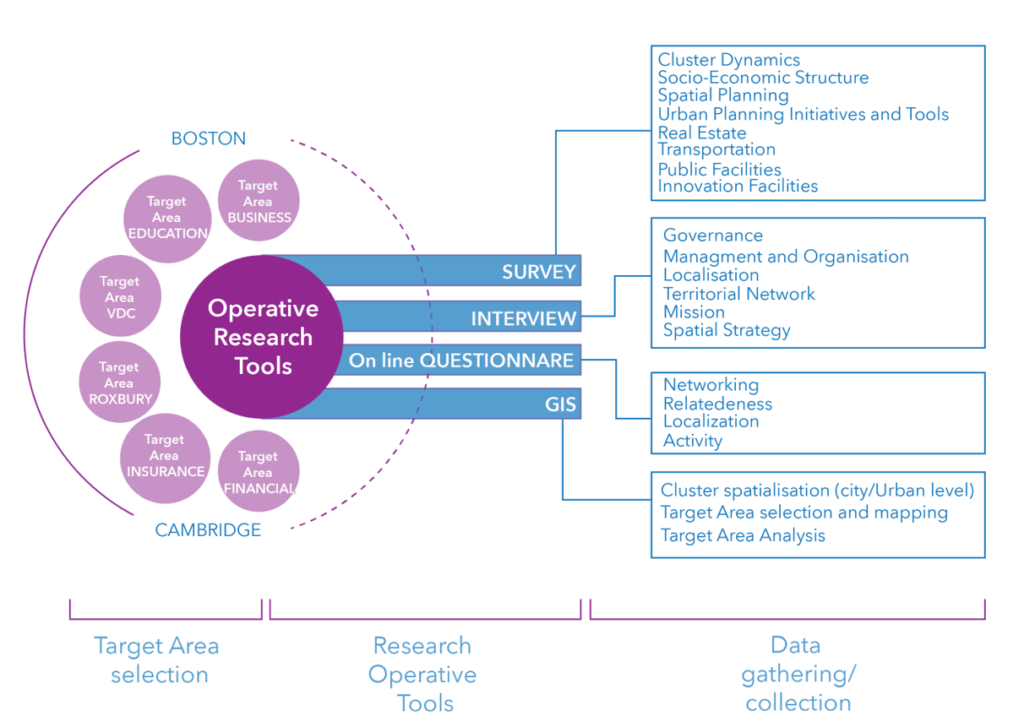
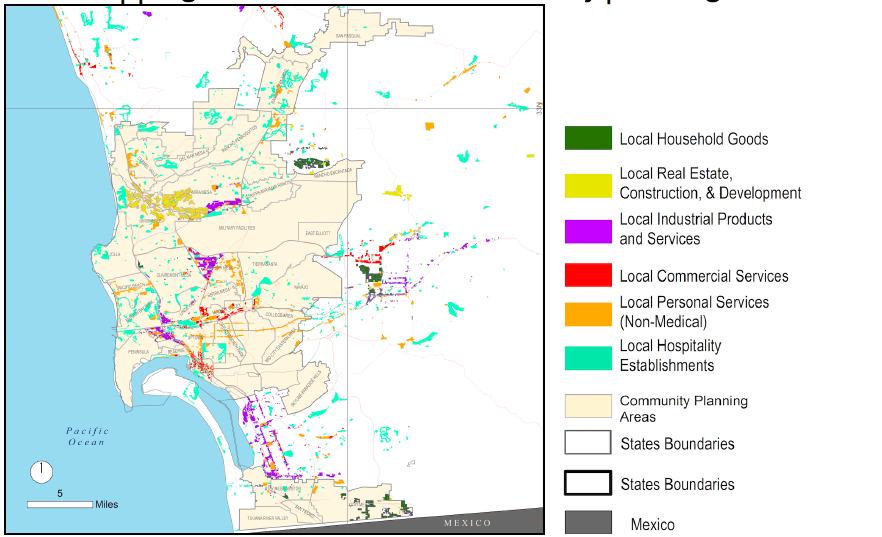
MAPS-LED Project
Multidisciplinary Approach to Plan Smart Specialization Strategies for Local Economic Development
MAPS-LED is a Marie Sklodowska-Curie RISE research project funded by the European Union’s HORIZON 2020 program for Research and Innovation.